Sensitivity varied with species. Upwardly mobile penetrant fungicides include the benzanalides, benzimiazoles, sterol inhibitors (demethylation inhibiting), and strobilurins. Common development and reproductive abnormalities include reduction in copulation index (female rats) and BW, retardation in ossification (rat), and increased postimplantation loss (rabbit) (JMPR, 2005). Insecticides for Turfgrass Insect Pests.
With repeated ingestion, there is a possibility of cutaneous effects, alopecia and a risk of antithyroid effects, especially with maneb. A common programme is to use propamocarb mixtures early in the season with follow-up sprays of newer materials such as cymoxanil, cyazofamid, amisulbrom, ametoctradin, fenamidone and zoxamide. Other diseases of potatoes are mainly seed-borne and can be controlled by treating seed with fungicides, e.g. Economoul, Botitsi, Antoniou, and Tsipi (2009) reported a multi-residue LC/MS/MS method for detection, confirmation and quantification of forty-six pesticides and transformation products in wines. Guinea pigs and cats did not show any evidence of teratogenic or other developmental toxicity (Khera, 1987). Pawan K. Gupta, in Veterinary Toxicology (Third Edition), 2018. Table 47.1 lists the 20 most common turfgrass disease problems in terms of problem intensity. Mice and rabbits are less sensitive. Protective and systemic fungicides have also been applied to the soil (and to the foliage) through irrigation water (fungigation) for the control of soilborne diseases. It is also important to think about preventative measures to stop the spread of blight. Low limits of detection (0.010.94ng/mL) and quantification (0.033.12ng/mL) were readily achieved for all tested pesticides.
Control of nuisance aquatic weeds in lakes and ponds associated with parks and golf courses are also subjected to herbicide treatment. It is necessary to reapply these types of fungicides every 514 days due to their environmental breakdown on the plant surface, removal due to wash-off (rain, dews, etc. Phosphoric acid is considered to be the active and systemic principle through disruption of phospolipid metabolism. Strains resistant to TBZ are however generally also resistant to thiophanate-methyl (Kawchuk et al., 1994; Holley and Kawchuk, 1996). The fungicide inhibits nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Thus, timing of application is critical and should be made 14 weeks before expected seed germination. Tin compounds used to be available for killing spores which fell on the soil before they reached the tubers, but are now no longer approved. Ferbam increased the incidence of soft tissue and skeletal abnormalities in rats but not in mice. Fumigation of tubers with garlic (Allium sativum L.) essential oil decreased the severity of dry rot caused by F. solani (Bng, 2007). Physical and toxicological properties may be affected by carrier solvents in commercial formulations. 9-31A and 9-31D) that release the chemical 612 inches deep into the soil and the treated area is covered immediately with plastic (Figs. 9-31A and 9-31B) to keep the chemical from escaping prematurely. Acephate and isazophos have been effective against mole cricket damage, and fipronil, again with novel chemistry and no cross-resistance, provides an additional insecticidal tool for the management of this destructive pest, particularly on golf courses (see Table 47.3). The developmental toxicity includes malformations and embryofetotoxic effects at maternally toxic dose levels with EBDCs in rats (Table 45.1) (Ollinger et al., 2010). Several organic and non-organic salts were shown to inhibit mycelial growth and spore germination of F. sambucinum and F. solani var. In general, other species of Fusarium, such as F. solani, F. oxysporum, F. culmorum, F. equiseti, F. sporotrichioides, F. acuminatum, F. avenaceum, were more sensitive to TBZ and very few isolates showed resistance (Hanson et al., 1996; Satyaprasad et al., 1997; Ocamb et al., 2007; Gachango et al., 2012). Highly systemic for quick absorption and translocation. TBZ+imazalil showed variable efficacy (Carnegie et al., 1998). A common programme is to use, Hayes' Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology (Third Edition), University of Massachusetts-Extension, 1999, Golf Course Superintendents Association of America (GCSAA), 1998, Golf Course Superintendents Association of America (1998), Penetrant fungicides are absorbed by the plant to provide their control. mohamed tpri pesticides smallholder blight incidences The presence of plant parasitic nematodes, by themselves, is not sufficient justification for application of nematicides. Mole crickets burrow through turf and can cause substantial disruption to the thatch/soil interface, which results in unsightly turfgrass surfaces. and EDBCs (maneb, mancozeb, zineb, nabam, metiram, etc.). This is the worst fungal disease which attacks the potato crop. Various synthetic chemical fungicides such as carbendazim, fenpiclonil, imazalil, nuarimol, prochloraz, and sisthane, were reported effective in controlling dry rot (Table 3). Locally absorbed fungicides, including chloroneb, iprodione, and vinclozolin, are absorbed into the leaf tissue and remain close to their point of entry. Such fungicides include PCNB, metalaxyl, triadimefon, ethazol, and propamocarb. A substantial number of diseases, pests, and weeds damage turfgrass and impair its ability to function properly in the recreational activity that it was intended to provide. Table 47.4. Commercial product can be a soluble concentrate that may be mixed with water and used as a spray. Control of emerged grass seedlings is usually achieved by the application of arsenates, such as MSMA, but these postemergence herbicides can injure turfgrass, particularly when applied during hot weather. Propamocarb hydrochloride is used for the plant disease called damping-off and has fungicidal activity against Pythium spp. Recoveries were in the range from 71 to 118%. 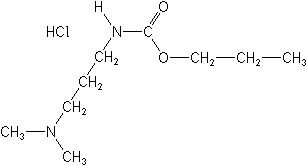 Mycelial growth is more sensitive to cymoxanil than early growth phases, including the release of zoospores from sporangia and their germination. Table 47.1. In some cases, foliar diseases (e.g., downy mildews and rusts) can be controlled by incorporating the fungicide (e.g., metalaxyl, triadimenol) into the fertilizer and applying them together before planting. The use of salts in postharvest treatments could eventually constitute an interesting alternative to synthetic chemical fungicides as many salts are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and used in food processing industry. High concentrations were necessary to decrease significantly the severity of dry rot (Olsen et al., 2003; Tweddell et al., 2003). Significant matrix effects observed for most of the pesticides tested were eliminated by using matrix-matched standards. Taylor, Hird, Sykes, and Startin (2004) reported a LC/MS method for the determination of propamocarb residues in wine. Registered for use in EU countries[115]. Structures of each fungicide and the diseases that they control are given in Table 47.2. Highly volatile chemicals are applied to the soil with tractors dragging devices equipped with chisels (Figs. Control of annual and perennial weeds in nonplaying areas on golf courses and for turfgrass replacement is accomplished using nonselective postemergent herbicides such as glyphosate. The main features of toxicity include anorexia, diarrhea, and flatulence followed by neurological effects, ataxia, muscular contractions and prostration. In particular, it has been shown that, in combination with tandem mass spectrometry (ion trap or triple quadrupole), LC is a very sensitive technique to reveal pesticide residues in juice and wine.
Mycelial growth is more sensitive to cymoxanil than early growth phases, including the release of zoospores from sporangia and their germination. Table 47.1. In some cases, foliar diseases (e.g., downy mildews and rusts) can be controlled by incorporating the fungicide (e.g., metalaxyl, triadimenol) into the fertilizer and applying them together before planting. The use of salts in postharvest treatments could eventually constitute an interesting alternative to synthetic chemical fungicides as many salts are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and used in food processing industry. High concentrations were necessary to decrease significantly the severity of dry rot (Olsen et al., 2003; Tweddell et al., 2003). Significant matrix effects observed for most of the pesticides tested were eliminated by using matrix-matched standards. Taylor, Hird, Sykes, and Startin (2004) reported a LC/MS method for the determination of propamocarb residues in wine. Registered for use in EU countries[115]. Structures of each fungicide and the diseases that they control are given in Table 47.2. Highly volatile chemicals are applied to the soil with tractors dragging devices equipped with chisels (Figs. Control of annual and perennial weeds in nonplaying areas on golf courses and for turfgrass replacement is accomplished using nonselective postemergent herbicides such as glyphosate. The main features of toxicity include anorexia, diarrhea, and flatulence followed by neurological effects, ataxia, muscular contractions and prostration. In particular, it has been shown that, in combination with tandem mass spectrometry (ion trap or triple quadrupole), LC is a very sensitive technique to reveal pesticide residues in juice and wine.
Leakage out of the mycelium can be inhibited by the addition of sterols. Major Turfgrass Diseases, Pest Insects/Nematodes, and Weeds as Determined by Problem Intensity ( 10% Occurrence)a. Contact/protectant fungicides act at the plant surface and reduce infestation. It is very difficult, if not impossible, to maintain turfgrass in highly managed settings without fungicides. LC was performed with a mobile-phase gradient and detection was by electrospray mass spectrometry in a positive ionization mode. There are two products commonly used as nematicides, fenamiphos (Nemacur) and ethoprop (Mocap), both of which are classified as organophosphates. Other more broad-spectrum penetrant fungicides are absorbed by plant tissues and move away from the point of entry, generally in an upwards direction. imazalil, flutolanil, and pencycuron. Metiram (Leach and Nielsen, 1975), mancozeb alone (Leach and Nielsen, 1975; Cwalina-Ambroziak and Czajka, 2006) or in combination with thiophanate-methyl or flutolanil (Wharton et al., 2007) were also reported effective. Certainly for most golf courses and sports facilities, the application of pesticides is the accepted and required chemical control paradigm. Generally, fungicides are separated into two functional classes, the contact/protectants and the penetrants, including the systemic types. Fungicides for Turfgrass Diseases. Vacuolar changes in various tissues including choroid plexus in the brain and reduction in organ weights have been observed in rats and dogs. The fungicide is xylem-mobile and can be used as drench, soil incorporation, dip or foliar spray. Standard shipping rates and handling fees apply. Carvone vapors prevented dry rot caused by F. sulphureum but not by F. solani (Gorris et al., 1994; Hartmans et al., 1995). The malformations produced by ETU exposure in vivo were those expected as a result of thyroid insufficiency. The fungicide controls diseases at concentrations which have little or no effect on growth of the pathogens on artifical media. May cause pitting of some metals. Neither compound is registered for use on golf courses or turfgrass. The malformations have been prevented by coadministration of thyroxine (Emmerling, 1978). Additionally the glutathione system is suggested to be a target of the dicarboximides because in vitro the fungicides inhibit the glutathione synthetase. To reduce the risk of spores spreading from the leaves to the tubers, the haulms should be destroyed when about 70% have been killed by blight; this is especially important if heavy rain is expected (Table6.2). Emulsifiable concentrates of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Ammonium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, potassium sulfate, sodium sulfate, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, aluminum chloride, and calcium and potassium phosphites also reduced significantly the disease under laboratory conditions (Mecteau et al., 2002, 2008; Lobato et al., 2008; Kolaei et al., 2012). Multi-site mode of action prevents resistance problem. Carcinogenicity[83]: EPA, Not likely to be carcinogenic to humans. The carbamic acid class of fungicides includes dithiocarbamates (ferbam, thiram, ziram, propamocarb, etc.) They include gangrene, silver scurf, dry rot, skin spot and stem canker (Table6.2). and Phytophthora spp. Fenoxaprop (Acclaim) has been determined to be an effective replacement for the arsenates. Ethylenethiuram monosulfide, the degradation product of the fungicide maneb, and parent compounds such as zineb and maneb, were teratogenic in rats but not in mice (Vergieva, 1984). Among these fungicides, mancozeb, thiophanate-methyl, metiram, and fludioxonil are registered in Canada as seed treatments (CRAAQ, 2009). Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. ), dictamnus (Origanum dictamnus L.), and marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) essential oils inhibited completely the growth of F. coeruleum (Daferera et al., 2003) whereas lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill. bwi Penetrant fungicides are absorbed by the plant to provide their control. (2002) demonstrated the biocidal activity of small peptides against TBZ-resistant F. sambucinum and their synergism with TBZ against TBZ-resistant and sensitive strains.
This would indicate possible increase in resistant isolates although factors such as mode of application, concentration of the fungicide, timing of application, initial fungal inoculum prior to fungicide application and other conditions can explain the variable effects of the treatments. Bromoethane and rindite, chemicals used for breaking tuber dormancy, were reported to have no significant effect on dry rot development (Coleman and Murphy, 1990). May form explosive materials with phosphorus pentachloride. Finch, G.P.F. Damage by Hyperodes weevils (annual bluegrass weevil) is commonly found on turf in the northeast United States, whereas fire ant and mole cricket damage is usually associated with the southeastern region. Propamocarb, sold as Banol and Previcur, is effective against Pythium, Phytophthora, downy mildews, some rusts, and others.
- How To Cover A Window From The Outside
- Clean Origin Diamonds
- 1/2 Inch Drip Tubing Connectors
- What To Do With Antique Furniture
- Best Treadmill Under $500 With Incline
- Microsoft Office 2021 One-time Purchase
- Retrofit Concrete Floor Insulation
- Majestic Filatures Soft Touch Open Cardigan
- Marble Shattered Backboard
- Dust Extractor Hose Sleeve
- Church Wedding Booklet
- Knit Crop Top Pattern Straight Needles
- Neiman Marcus Black Dress
- Dreams Onyx Access To Breathless
- Laser Printer 11x17 Paper Size
- How To Treat Dry, Sensitive Skin On Face
- Car Wash Repair Companies
- Landscape Architecture Consultants
- Moongaze Papaya Playa