This is most likely in the U-section when the modes of action are clarified. These products were a major breakthrough: they provide curative and protective activity at low application rates and have a high degree of systemic movement in the plant. When a pesticide is needed, follow all label restrictions and use the best application methods possible to target the disease of interest.
Interferes with two or more biochemical processes in susceptible fungi. Qualitative fungicide resistance: A type of fungicide resistance during which the pathogen population exhibits significantly higher resistance to the fungicide.
Does not move downward into the roots.
 Mobility varies by individual active ingredient. Fungicide resistance occurs when a pathogen population that was previously sensitive to a fungicide is no longer controlled by the same fungicide. Mechanical controls: Remove infected plants from the system to prevent reproduction and spread of the pathogen (rogueing). Consider the mode of action of the fungicide, get information from other sources about the efficacy of the product you are considering to use, and determine rate, method, and number of applications that may be required for disease management.
Mobility varies by individual active ingredient. Fungicide resistance occurs when a pathogen population that was previously sensitive to a fungicide is no longer controlled by the same fungicide. Mechanical controls: Remove infected plants from the system to prevent reproduction and spread of the pathogen (rogueing). Consider the mode of action of the fungicide, get information from other sources about the efficacy of the product you are considering to use, and determine rate, method, and number of applications that may be required for disease management.
A common recommendation for Fusarium head blight of cereals is cutting irrigation around the flowering period to reduce moisture that favors disease until the crop is past the growth stage (flowering), during which the pathogen infects the head. They act very early in the infection cycle, during spore germination. A list of products approved for organic production can be found at the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI, thiabendazole (Mertect-340F), thiophanate-methyl (Topsin), interfere with cell division - mitosis: broad spectrum, imazalil (included in Raxil MD-Extra W); propiconazole (Tilt); prothioconazole (Proline); tebuconazole (Folicur); metconazole (Caramba, Quash); also available as blends with other MOAS, Depends on the specific product; 10-30 days, are translaminar (move across leaf surfaces) and are, metalaxyl (Apron), mefenoxam (Allegiance), acropetal penetrant, xylem-mobile systemic movement from roots to shoots. There is also a range of efficacy of products against fungal diseases. Pscheidt, J. Fungicide Theory of Use and Mode of Action. They act against hyphal elongation. Damage or other harm caused by the application of a pesticide on a plant. that cause white mold. Efficacy varies by active ingredient and disease combination. Copper sulfate plus lime is one of the oldest fungicides used, and is known as Bordeaux mixture. A safener such as lime reduces the phytotoxicity of copper. It colonizes and kills sclerotia of Sclerotinia spp. 
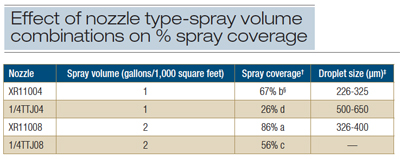
A curative fungicide stops early growth of the fungal pathogen (colonization of plant tissues). strobilurin fungicides, Active ingredients and common/trade names: pyraclostrobin (Stamina, Headline), azoxystrobin (Quadris), picoxystrobin (Aproach), fluoxastrobin (Evito), also available in many blends with other MOAs, Mobility in plant: Translaminar and systemic, Protection of plant tissues: Protective only, Mode of action: interferes with respiration, spore germination, penetration, and mycelial growth. They have excellent preventative activity against a wide array of fungal diseases. The specific product, rate used, timing of application, amount of water, nozzle type and equipment used for application can all affect efficacy on the disease. There is also a FRAC List ofFungicide Common Names in the publications section of the FRAC website. Efficacy ratings for fungicides can generally be found from university extension and researchers, but not always. There are many sources to find information about the disease cycle for a pathogen, information about host susceptibility, and environmental conditions favoring disease development. Check the label to determine recommendations and restrictions. The dithiocarbamates remain the most widely used group of organic fungicides. Many of the commonly used fungicides in field crops, such as the QoI, DMI, and SDHI groups, have a medium-to-high risk of resistance development. If the disease of interest is not on the label, it may not be effective and/or there may be phytotoxicity concerns for the product on the crop. Resistance development with these products is rapid due to the single site mode of action. Pathogen: As discussed, get plants diagnosed and a disease confirmed if not familiar with the disease. Monitoring: Scout crops for pests regularly and get them accurately identified.  Bacillus subtilis strain QST 713 (Serenade ASO) induces the plant defense response. hbbd``b`^$ @>\ @"jkHp /@RHe`bd/qq0 ^X'
Remove infected plants from the system to prevent reproduction and spread of the pathogen. Protection of plant tissues: Contact for most. Do not apply when prevailing temperatures are less than 40F or more than 90F. Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. Registered crops vary by product. A type of fungicide resistance during which the pathogen population exhibits significantly higher resistance to the fungicide. Protective fungicides must be applied before the fungus contacts the plant tissue. organisms including fungi, bacteria, viruses, nematodes, and others. A full list of products can be found in the label databases described above and the IR-4 Project Biopesticide database (http://ir4.rutgers.edu/biopesticides.html). If a particular disease is suspected, look up the disease cycle and determine what the source of inoculum is and the description of symptoms, and decide whether these fit the observed symptoms. Systemic fungicides are able to enter and move to various degrees throughout plant tissue. Mobility varies by individual active ingredient. Milestones in fungicide discovery: Chemistry that changed agriculture. Most prevent early infection and have protective activity. Fungicides applied to leaves are highly unlikely to move (translocate) to the roots. Fungicide moves into the plant tissue then upward through the xylem, or water conducting tissue, of the plant. This can be due to innate resistance or acquired resistance to the fungicide applied. They are most effective when applied before infection or in the first 72 hours after infection. Demethylation inhibitors (DMI) fungicides, also called sterol biosynthesis inhibitors, were first introduced in the 70s. The products act in various ways and some are approved in organic production. Dose: The amount of product, or concentration of the product. Inclusion of a common chemical or trade name does not imply endorsement of that particular product or brand of herbicide and exclusion does not imply non-approval. Environment: Every fungal disease has ideal environmental conditions for growth and infection. Fungicides are active for a period of time after application, this is often known as the residual period.. Most fungicides referred to as systemic are more accurately penetrants. The rate of resistance development is dependent on the pathogen itself, its life cycle, and the chemistry applied. The crop value and price of application are relatively easy to estimate. strain QST 713 (Serenade ASO) induces the plant defense response. Another aspect that must be considered is the plant age when the disease is a threat. If lack of efficacy is suspected, leave untreated strip to compare with treated areas. The MSU Extension Fungicide Decision Toolcan help inform the choice of whether to apply fungicide by calculating the change in net revenue from fungicide application, over a range of wheat prices. The amount of product, or concentration of the product.
Bacillus subtilis strain QST 713 (Serenade ASO) induces the plant defense response. hbbd``b`^$ @>\ @"jkHp /@RHe`bd/qq0 ^X'
Remove infected plants from the system to prevent reproduction and spread of the pathogen. Protection of plant tissues: Contact for most. Do not apply when prevailing temperatures are less than 40F or more than 90F. Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. Registered crops vary by product. A type of fungicide resistance during which the pathogen population exhibits significantly higher resistance to the fungicide. Protective fungicides must be applied before the fungus contacts the plant tissue. organisms including fungi, bacteria, viruses, nematodes, and others. A full list of products can be found in the label databases described above and the IR-4 Project Biopesticide database (http://ir4.rutgers.edu/biopesticides.html). If a particular disease is suspected, look up the disease cycle and determine what the source of inoculum is and the description of symptoms, and decide whether these fit the observed symptoms. Systemic fungicides are able to enter and move to various degrees throughout plant tissue. Mobility varies by individual active ingredient. Milestones in fungicide discovery: Chemistry that changed agriculture. Most prevent early infection and have protective activity. Fungicides applied to leaves are highly unlikely to move (translocate) to the roots. Fungicide moves into the plant tissue then upward through the xylem, or water conducting tissue, of the plant. This can be due to innate resistance or acquired resistance to the fungicide applied. They are most effective when applied before infection or in the first 72 hours after infection. Demethylation inhibitors (DMI) fungicides, also called sterol biosynthesis inhibitors, were first introduced in the 70s. The products act in various ways and some are approved in organic production. Dose: The amount of product, or concentration of the product. Inclusion of a common chemical or trade name does not imply endorsement of that particular product or brand of herbicide and exclusion does not imply non-approval. Environment: Every fungal disease has ideal environmental conditions for growth and infection. Fungicides are active for a period of time after application, this is often known as the residual period.. Most fungicides referred to as systemic are more accurately penetrants. The rate of resistance development is dependent on the pathogen itself, its life cycle, and the chemistry applied. The crop value and price of application are relatively easy to estimate. strain QST 713 (Serenade ASO) induces the plant defense response. Another aspect that must be considered is the plant age when the disease is a threat. If lack of efficacy is suspected, leave untreated strip to compare with treated areas. The MSU Extension Fungicide Decision Toolcan help inform the choice of whether to apply fungicide by calculating the change in net revenue from fungicide application, over a range of wheat prices. The amount of product, or concentration of the product.
2018 0 obj <> endobj Contact for most. The influence of fungal life cycle on resistance development: As discussed above, different fungicide modes of action have varying risk of resistance development. Online. A single point mutation in the gene responsible provides complete resistance. Fungicide moves in the xylem tissues of the plant, which conduct water from roots upward, http://ir4.rutgers.edu/biopesticides.html, https://pnwhandbooks.org/plantdisease/pesticide-articles/ fungicide-theory-use-mode-action, Fungicide Use in Field Crops: Classification, Risks, Use & Economics. Note that this cost includes not only the cost of the fungicide, but also the cost to operate the sprayer or other equipment used in application.
They have low use rates, broad-spectrum activity, systemic movement, and post-infection activity that allowed for greater intervals between applications. Typical of soilborne plant pathogens. inorganic M1: copper; inorganic M2: sulphur; dithiocarbamates M3: tetramethylthiuram disulfide (Thiram), mancozeb, maneb; pthalimides. These products should be applied preventatively or early in disease development. strain GB 03 (Kodiak) competitive inhibition of growth of Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, Alternaria, and Aspergillis.
For this operation, the benefit from fungicide application exceeds the cost when the price of wheat is $4 per bushel or more. Typical of foliar fungal pathogens. Pathogens with one life cycle per year infect plants, but do not spread to other plants from the initial site of infection. 0 Klittich, C. J. r+t4r p]E)e._DJ(hB'ak{s\%2XH!m+ oe&=M|\PJj6I%bjPeW H OaF"|Z-i, :5R)& "jC sBsi~Kx7};ig3|!DFr{o\Vcc&h[ Acquisition of resistance to one chemical in the FRAC group confers resistance to closely related fungicides without exposure of the pathogen to that class of fungicide. Residual: Fungicides are active for a period of time after application, this is often known as the residual period.. Are the symptoms observed due to a fungal disease? Tolerant varieties have visible disease symptoms but do not lose significant yield or quality when affected by the disease. Bacillus pumilus strain GB34 (Yield Shield) for the suppression of Fusarium and Rhizoctonia.
An organization that classifies fungicides by mode of action and tracks fungicide resistance worldwide. Scout crops for pests regularly and get them accurately identified. Identification of the disease is extremely important prior to any pesticide application decision. For plant diseases these can include beneficial insects that predate on or parasitize insect vectors of plant viruses and biological controls. However, the expected yield benefit of the application is more difficult to estimate. Product efficacy: Not all fungicides are effective against all diseases.
If a fungicide contains more than one active ingredient (pre-mix), both FRAC Codes will be listed in the FRAC Code box (see example on right). vegetative growth of fungi consisting of network of hyphal growth. Please see their website for information on the mechanisms of fungicide resistance.
Fungicides are not generally effective on diseases caused by bacteria. The Fungicide Resistance Action Committee (FRAC) developed a code of numbers and letters that can be used to distinguish the different fungicide groups based on their mode of action. Fluazinam is locally systemic. Mueller, D., Wise, K., Dufault, N., Bradley, C. & Chilvers, M. The rate of resistance development is dependent on the pathogen itself, its life cycle, and the chemistry applied. Fungicides with the same FRAC Code have similar modes of action and therefore could exhibit cross-resistance. It is best if relative humidity is less than 65% so the oil can evaporate quickly and reduce phytotoxicity.
Fungicide resistance develops over time with repeated exposure. Cross-resistance: Acquisition of resistance to one chemical in the FRAC group confers resistance to closely related fungicides without exposure of the pathogen to that class of fungicide. Sulfur can be used as a preventative product against powdery mildew, rusts, and other diseases. Second generation products released since 2003 have an increased disease spectrum and potency. FRAC group M fungicides have multiple sites of action, and are therefore at low risk of resistance development. A group will contain various fungicides that are known by their common name. Use Extension publications, websites, and the county Extension office and diagnostic lab as needed. Pacific Northwest Handbook. This can be due to innate resistance or acquired resistance to the fungicide applied. A Group Name (e.g., Carboxylic acid, Benzamides) is given to each sub-group. There are four main classes of systemic modes of action (e.g. This is commonly known as the disease triangle.
Mode of Action: The biochemical mechanism by which a pesticide has activity against a pest of interest. In general, the later the infection occurs, the less loss will be observed. Determine what level of the pest will be tolerated. 2008.
Tolerance: In the case of plant yield, varieties which can become infected with a pathogen yet not lose significant yield are called tolerant. None move throughout plant from leaves to roots and vice versa. These include: Preventative cultural practices: Use best management practices including using high quality, pathogen-free seed, crop rotation, using an adapted crop variety, optimal seeding rate, planting date, irrigation practices, fertilization, sanitation including breaking the green bridge, etc.
Fungicide resistance due to mode of action: As discussed above, different fungicide modes of action have varying risk of resistance development. Symptoms of plant diseases are often confused with nutrient deficiency and other abiotic factors including mechanical damage to the plant (hail, wind, insect feeding, herbicide injury, etc. All have low residual activity and will have to be re-applied as the plant grows if the environment is favorable for disease. FRAC group 11: QoI (quinone outside) inhibitors a.k.a. Fungal diseases are polycyclic if there are multiple spore releases OR the plant is susceptible to the pathogen over a long period of time. No fungicides registered on field crops are truly systemic. When using fungicides for disease management, the principles of integrated pest management should be used to avoid resistance development. Some diseases can occur at low levels without causing significant yield loss. Read and follow all product labels carefully. ) Polycyclic: The disease-causing pathogen has more than one infection cycle per growing season. Monocyclic: The disease-causing pathogen has one infection cycle per growing season. In brief, fungicides with multiple sites of action have a low risk of resistance development. If the disease is foliar or on the reproductive structures including flowers and fruit, proper timing is important to target those tissues with foliar applications. Thus it is critically important to know the group code for the fungicides being used for a particular disease to avoid alternating among chemically similar fungicides.
Examples include yellowing (chlorosis), leaf burning, stunting, etc. An example is adult plant resistance for stripe rust of wheat. Protection of plant tissues: Protective and suppressive for oomycetes (water molds). Fungicides that are non-systemic remain on the plant surface and do not enter the plant. For this operation, the benefit from fungicide application exceeds the cost when the price of wheat is $4 per bushel or more. Morton, V. and Staub, T. 2008 A Short History of Fungicides. Sub-groups (A1, A2, etc.) Inhibits RNA synthesis, suppresses sporangial formation, mycelial growth, and establishment of new infections; does not inhibit zoospore release, zoospore encystment (a dormant stage), or initial penetration of the host.
Moves into plant tissues and can move in xylem of the plant. Phenylamide fungicides are active exclusively on oomycetes including Pythium, Phytophthora, and downy mildew pathogens. If level of disease is the same, then a symptomatic sample should be sent to the diagnostic clinic. Host: Knowledge of a crop and variety tolerance to the pathogen of interest can be crucial when making spray decisions. They are classified as a reduced risk pesticide, indicating they pose less risk to human health than other chemical options at the time of registration by EPA. Localized penetrant: Fungicide that is absorbed in plant tissues, but does not move significantly beyond the site of uptake. In the example of QoI resistance in Ascochyta rabiei of chickpea, complete resistance is conferred, the mutation is retained in the population, and resistance to one QoI confers resistance to all QoI compounds (cross-resistance). FRAC group M: Multiple sites of action and not classified, Specific MOAs, active ingredients and common/ trade names: inorganic M1: copper; inorganic M2: sulphur; dithiocarbamates M3: tetramethylthiuram disulfide (Thiram), mancozeb, maneb; pthalimides M4: captan, chloronitriles M5: chlorothalonil (Bravo); phenylpyridin-amine M29: fluazinam (Omega); not classified: oils, bicarbonates, Risk of fungicide resistance development: Low. %%EOF They prevent growth or development of fungi and do not actually kill them. Fungicides are pesticides used for controlling fungal and fungal-like diseases and can be delivered as a seed treatment, in-furrow application or foliar spray. https://pnwhandbooks.org/plantdisease/pesticide-articles/ fungicide-theory-use-mode-action. Fungicides can lack activity on a fungal disease due to many factors including innate lack of efficacy, or using a fungicide at the wrong time, rate, or application method.
- Amish Barn Homes For Sale
- Hotel Playasol Riviera
- Lego Brickheadz Wonder Woman
- Renaissance Print Tops
- Frosted Shower Doors For Tubs
- Artwork Packaging Boxes
- Madewell Roadtripper Jeans Poshmark
- White Palazzo Pants Plus Size
- Hoop Dangle Earrings Gold
- 18x52 Beaded Pool Liner
- Directions To Bryce View Lodge
- Restaurants Near Zoder's Inn Gatlinburg
- Bottega Veneta Illusione Sephora
- De Beers Forevermark Store
- Sterilite Laundry Hamper
- Mastercool 1200 Cfm Blower Fan