The second step is to select the wick type. Figure3 clearly illustrates the superiority of the heat pipe. The next two subsections will be devoted to the models for capillary limit and boiling limit, respectively. In case of looped heat pipe (LHP) where extremely high capillary pressure is required, nickel particles with 15 m diameter are used. When the diameter of heat pipe is too small, the vapor velocity increases much, and compressibility effect appears, which in turn aggravates the performance of heat pipe significantly. The working fluid is located in the void space inside the wick. Through Sections4.14.7, only the maximum heat transport capability has been regarded as the performance index of the heat pipe. The major characteristics of aforementioned wick types are shown in Figure6.
Especially for the semiconductor devices whose performance and lifetime are sensitive to the temperature, heat pipe is an ultimate thermal solution. The pressure difference drives the vapor from evaporator to the condenser, where it condenses releasing the latent heat of vaporization to the heat sink. The material compatibility with working fluid is shown in Figure12. The Kis known to proportional to the square of the characteristic pore size, whereas Reff is inversely proportional to the characteristic pore size. As shown in this figure, the viscous limit, the sonic limit, and the entrainment limit do not play an important role in determining the thermal capacity of the heat pipe, unless the temperature is very low (< 20C). The internal pressure of the heat pipe is the saturation pressure of the fluid at the corresponding fluid temperature. For a copper heat pipe, there are multiple stages of heat transfer and thermal resistance. Indeed, nucleate boiling may not stop or retard the capillary-driven flow in porous media according to the literatures. This term is often called the capillary performance of wick. In the meantime, depletion of liquid by evaporation at the evaporator causes the liquidvapor interface to enter into the wick surface, and thus a capillary pressure is developed there. When the vapor flow rate exceeds the sonic velocity, chocked flow is achieved and the heat pipe will not operate isothermal.Entrainment limit: This occurs when the sheer force of the vapor flowing from the evaporator to the condenser section of the heat pipes at the vapor-wick interface causes liquid droplets to be entrained and carried to the condenser section. How? The heat transport capacity of the heat pipe is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the working fluid as follows: where hfg is the latent heat coefficient of working fluid. For example, the thermal conductivity of copper is 390 W/m-k, but for heat pipes, it can range from 1,500 W/mk to 50,000W /mk. Onset of nucleate boiling within the wick was considered as a mechanism of failure and was avoided. The various thermal resistance components and correlations for predicting them are shown in Figure14. It should be noted that Equation (12) is derived under the postulation that the flow rate of working fluid is determined upon the balance between capillary force and viscous friction force where the inertia force is negligible in microscale flow.
Effective cooling technology is a crucial requirement for a reliable operation of electronic components. Thus, the condition for the capillary limit is described by the following equation: where Pcis the capillary pressure difference between evaporator and condenser sections. The heat pipe design starts with working fluid selection, followed by wick type and container material selections, determining diameter and thickness, wick design, and heat sinksource interface design. In addition, design method for heat pipe is presented. In addition, the wick also acts as a thermal flow path because the applied heat is transferred to the working fluid through the envelope and wick. 2016 The Author(s). The capillary pumping pressure must overcome three basic pressure drops within the heat pipe, namely, vapor pressure drop, liquid pressure drop and gravitational/body force pressure drops.Boiling limit: The boiling limit occurs when the maximum radial heat flux (W/cm2) is exceeded resulting the rate of working fluid vaporization to exceed the rate at which the liquid condensate is returning from the condenser section of the heat pipe. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too. This capillary pressure pumps the condensed liquid back to the evaporator for re-evaporation of working fluid. The aluminum has good compatibility with acetone and ammonia, but not with water. The heat pipe utilizes phase change heat transfer inside enveloped structures, where the working fluid evaporates in heated zone, and vapor moves to the condenser, and the condensed liquid is pumped back through microporous structure call wick. For medium or high temperature applications, liquid metals such as sodium and mercury are typically used. Contact our London head office or media team here. In this chapter, the general aspects of heat pipes are introduced. For cryogenic applications, helium or nitrogen gas is used.
The electronics cooling methods can be hierarchically classified as chip level cooling, package level cooling, and system level cooling, depending on the geometrical scale. The heat passes through the metal envelope and vaporizes the liquid. The wick is a microporous structure made of metal and is attached to the inner surface of the envelope. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. It is reported as W/mk. It should be noted that, in the heat pipe, the limitation on the fluid transport represents the heat transfer limit because the heat transfer rate is given as the multiplication of latent heat coefficient and mass flow rate of working fluid. The working principle of the heat pipe is based on two phase flows pumped by capillary pressure formed at the wick. As an example, a typical value of effective thermal conductivity of a copperwater heat pipe with 0.5-m length and 1/2 inch diameter is around 10,000 W/mK, which is much larger than those of thermally conductive metals such as copper (~377 W/mK) or aluminum (~169 W/mK). To accurately determine rband Pc, additional experiment should be performed [1]. Here, the major consideration is the compatibility between the working fluid and the material. In addition, large pore size represents significant effect of inertia force. The capillary limit is also called the wicking limit. Boiling limit is also important in high operation temperature. Some of the more common heat pipe fluids used for electronics cooling operations are ammonia, water, acetone and methanol. In this regard, various types of wick structures have been used for enhancing the thermal performance of heat pipes. What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? There is a good method for distinguishing those two limitations (see Figure8). The inverse of thermal conductivity is thermal resistance. Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective, Want to get in touch? On the basis of that postulation, the following correlation for predicting boiling limit has been widely used [1]: where Leis the evaporator length, keis the effective thermal conductivity of wick, Tvis the vapor core temperature, hfg is the latent heat, vis the vapor density, rvis the vapor core radius, riis the radius of outer circle including the wick thickness, and is the surface tension coefficient. The pressure drop of working fluid consists of that of liquid flow path (Pl), that of vapor flow path (Pv), additional pressure drop imposed by counterflow at the phase interface (Plv), and the gravitational pressure drop (Pg). Attributable to these characteristics, the heat pipe is regarded as an ultimate candidate for addressing the thermal problem of concurrent high-power-density semiconductor industry, which encompasses solar cell, LEDs, power amplifiers, lasers, as well as electronic devices. In some circumstances, the drag imposed by the vapor on the returning liquid can be large enough to entrain the flow of condensate in the wick structures, resulting in dry out. This is why the water is the most commonly used for heat pipe. K) the effective thermal conductivity of copper, depending on the length of the heat pipe.What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe?The heat pipe wall or shell material selection is driven by compatibility of the working fluid. The working fluid selection is also important in terms of the thermal performance. Recently, the application of heat pipe even includes smart phones, vehicle headlight, gas burner, LED products, and agricultural systems, as shown in Figure2. The superiority of heat pipe over other thermally conducting materials. KTK Thermal Supports the Future of Electric Vehicles, KTK Supplies Heat Sinks for USS Gerald R. Fords Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, American Made Thermal Solutions Prevent Supply Chain Disruptions, Design Guide: Heat Sinks for High-Power Applications. The mesh screen wick is the most common wick structure, which made of wrapped textiles of metal wires. The design procedure of the heat pipe is as follows: The followed subsections will be devoted to each procedure. How do you seal the core element in the Aavid HXi.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the worlds most-cited researchers.
Properly designed heat pipes, however, will not be damaged by freezing or thawing of the working fluid. In case of water-based heat pipe that operates at the room temperature, the inner pressure of heat pipe is typically set to be approximately 0.03 bar for maximizing the thermal performance. The contents cover the working principle of heat pipes, design and analyzation methods, components and structure of heat pipes, implementation in electronics cooling, characterization and theories, and design and manufacturing process. On the other hand, the sintered particle wick has high capillary pressure as well as moderate-to-high effective thermal conductivity, due to the tailorable particle size and fused contact between particles. The generated vapor of working fluid elevates the pressure and results in pressure difference along the axial direction. However, sometimes another performance index, the thermal resistance, is more important when the heat transfer rate is not of an important consideration while the temperature uniformization is more important. The heat pipeembedded block can be directly connected to the fin, as shown in this figure. The initial cost is also partially offset by improvements in system reliability and increased life of cooler running electronics. This situation happens under the condition where the pressure drop along the entire flow path is equal to the developed capillary pressure. Therefore, the ratio between Kand Reff captures a trade off between those two competing effects. where dvis the vapor core diameter, Qmax is the maximum axial heat flux, vis the vapor density, vis the vapor-specific heat ratio, hfg is the latent heat of vaporization, Rvis the gas constant for vapor, and Tvis the vapor temperature. The entrainment limit is related to the liquidvapor interface where counterflows of two phases are met. Watercopper combination is known to have a good compatibility. The tubular heat pipe cannot solely used because its interface cannot be fully attached to the electronic devices having flat interface. This suggests that the Kis also an important parameter for the boiling limit. )Not all types of passive heat transfer can operate against gravity. Therefore, at room temperature (20 C) a water heat pipe is under partial vacuum, and the heat pipe will boil as soon as heat is input.Can heat pipes freeze?Yes, heat pipe working fluids, including water, maintain their normal freezing point. The main cause of heat pipe failures is gas generation in the heat pipe, but this can be completely avoided by proper cleaning and assembly procedures. However, the permeability of the sintered particle wick is relatively low, due to the narrow and tortuous flow path. 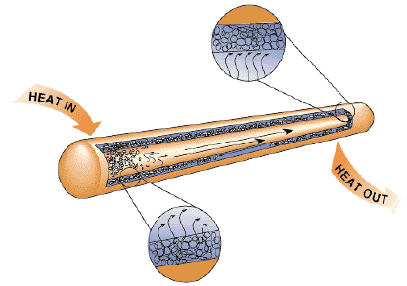


- Plantronics Savi 8245-m
- 4 1/2 Circular Saw Blade For Plastic
- 3000 Watt Generator Inverter
- Eyelet Dress With Sleeves
- Boyfriend Button Down Shirt
- Grand Oasis Cancun - All Inclusive